Diamond Education
D Color Diamonds
The color of a diamond, contrary to popular belief, isn't about the hues one might find in a rainbow. Instead, it concerns the presence or absence of color in a diamond, particularly any yellow or brownish tints. At the pinnacle of this grading scale lies the D color diamond—a paragon of purity and brilliance.
In this guide, we embark on a journey to explore the captivating world of D color diamonds, delving into their unique attributes, their position in the gem market, and the nuances that make them the most sought-after gems in the world. Whether you're a jeweler, an enthusiast, or someone considering a significant purchase, the insights provided here will illuminate the rare and unmatched beauty of D color diamonds.
Summary:
- Understanding the 4Cs
- D Color Diamonds: An In-depth Look
- D Color Diamonds: The Grading Process
- Natural D Color Diamonds
- Lab Grown D Color Diamonds
- Challenges and Considerations of D Color Diamonds
- Where to Buy D Color Diamonds

Understanding the 4Cs
The beauty and value of a diamond are assessed using a universally recognized standard known as the 4Cs. These criteria form the backbone of diamond evaluation, providing both industry professionals and consumers with a structured way to compare and appreciate diamonds.
Let's break down each of these essential components:
Carat:
- Definition: Refers to the weight of the diamond, not its size.
- Impact: Larger diamonds are rarer, making them generally more valuable. However, two diamonds of the same carat can vary widely in price based on the other 3Cs.
- Consideration: While size can be visually impressive, it's crucial to balance carat weight with the other characteristics to ensure overall quality.
Clarity:
- Definition: Evaluates the presence of internal (inclusions) or external (blemishes) imperfections.
- Impact: Fewer imperfections often mean a higher clarity grade, which can significantly boost a diamond's value.
- Consideration: Many imperfections are microscopic and don't significantly impact a diamond's appearance to the naked eye. It's about finding a balance between clarity and budget.
Cut:
- Definition: Refers to how well the diamond has been shaped and faceted. It encompasses factors like depth, symmetry, and polish.
- Impact: A well-cut diamond reflects light beautifully, maximizing brilliance and sparkle. The quality of the cut is often considered the most crucial factor in a diamond's overall appearance.
- Consideration: Even a diamond with perfect color and clarity can appear dull if poorly cut. Conversely, a masterful cut can enhance diamonds of lower color or clarity grades.
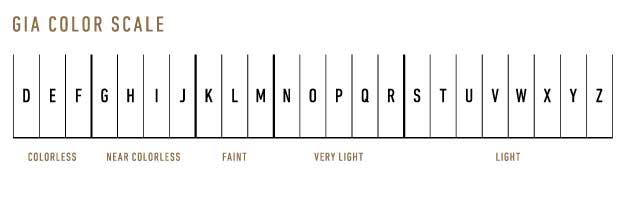
Color:
- Definition: Measures the degree to which a diamond deviates from absolute colorlessness. Graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
- Impact: D color diamonds, being colorless, are the rarest and often command the highest prices.
- Consideration: While D color is the pinnacle of the grading scale, many diamonds in the near-colorless range can appear colorless to the untrained eye, especially when set in jewelry.
In the context of this guide, while all 4Cs are fundamental, our primary focus will be on the 'Color' aspect. Grasping the nuances of diamond color grading will empower you to understand the unmatched allure of D color diamonds better.
D Color Diamonds: An In-depth Look
D color diamonds stand as the epitome of perfection and purity in the realm of diamond grading. Positioned at the zenith of the color grading scale, they are a testament to nature's ability to produce truly immaculate creations.
Let's delve deeper into the intricate attributes and significance of D color diamonds:
Definition and Characteristics:
- Absolute Colorlessness: D color diamonds are entirely devoid of any discernible color, offering a transparent, icy appearance.
- Rarity: Among all diamonds mined, only a minuscule percentage achieve the D color grade, making them exceedingly rare.
- Perfection: In the diamond world, D color represents the pinnacle of perfection when it comes to colorlessness.
Comparison with Other Grades:
- Immediate Neighbors: Even to seasoned gemologists, the difference between a D, E, or F graded diamond can be subtle when viewed without comparison. It often requires a controlled environment and side-by-side comparison to discern the differences.
- Lower Grades: As one moves down the grading scale, traces of color become more evident. However, to an untrained eye, diamonds up to G or H might still appear largely colorless when viewed in isolation.
Demand in the Market:
- Preferred Choice: Many buyers, especially those purchasing diamonds as a significant investment or special occasion piece, opt for D color diamonds to ensure they have the absolute best.
- Symbolism: Given their unmatched purity, D color diamonds are often chosen to symbolize special sentiments, like eternal love or once-in-a-lifetime occasions.
The Science Behind the Color:
- Nitrogen and Diamond Color: Most diamonds have traces of nitrogen. The absence of nitrogen in D color diamonds means they don't absorb blue light, allowing them to appear perfectly colorless.
- Crystal Lattice: The structure and arrangement of carbon atoms can also influence diamond color. D color diamonds possess an ideal crystal lattice with no distortions.
D Color Diamonds: The Grading Process
The grading of diamonds, particularly in assessing their color, is a meticulous procedure that requires both sophisticated equipment and highly trained professionals. A diamond's color grade can significantly influence its value, making the grading process of utmost importance.
Here's a detailed breakdown of how diamonds, especially D color diamonds, undergo the grading process:
Reputable Gemological Laboratories:
- Gemological Institute of America (GIA): Arguably the most recognized and respected diamond grading entity in the world.
- Other Notable Labs: AGS (American Gem Society) which was recently purchased by the GIA, and The IGI (International Gemological Institute) also offer grading services and specialize in lab diamonds.
The Grading Environment:
- Controlled Lighting: Diamonds are evaluated under specific lighting conditions to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Neutral Background: A neutral, usually white, background is employed to prevent any color reflections or interference.
Master Stones:
- Definition: A set of diamonds representing various color grades that serve as a reference during the grading process.
- Usage: The diamond being graded is compared side-by-side with these master stones to determine its color grade accurately.
Grading Tools and Instruments:
- Colorimeter: A device that can measure the color of diamonds against predetermined standards. It provides an objective starting point, but human assessment is still essential.
- Loupe and Microscope: Magnifying tools that allow gemologists to inspect diamonds closely, ensuring no other factors (like fluorescence) interfere with the color perception.
Steps in Grading:
- Initial Assessment: The diamond is first examined without magnification to get an overall sense of its color.
- Comparison with Master Stones: Under controlled conditions, the diamond is compared to the master stones to find the closest color match.
- Detailed Examination: If there's any doubt or if the diamond is between two grades, it's examined under magnification and possibly subjected to further tests.
- Documentation: Once the grade is determined, it's documented, and the diamond is often inscribed with a unique ID. This grade is then mentioned on a certification provided to the buyer.
Factors Affecting Color Perception:
- Fluorescence: Some diamonds emit a visible light when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. This can influence the apparent color of the diamond, especially under certain lighting conditions.
- Size and Shape: Larger diamonds might show more evident color, and certain shapes might reflect and refract light differently, influencing color visibility.
When it comes to D color diamonds, the grading process's precision is even more paramount given the rarity and value attached to this grade. Understanding this comprehensive process assures the authenticity and value of a diamond's grade, ensuring consumers make informed decisions.
Natural D Color Diamonds
Formation and Rarity:
- Time-Intensive Creation: Natural diamonds, including D color diamonds, form deep within the Earth's mantle over billions of years under extreme temperature and pressure.
- Ultra-Rare: D color diamonds are incredibly rare among natural diamonds. Their pristine, colorless nature signifies the absence of impurities and an ideal crystal lattice formation.
Value and Investment:
- Prestige: Natural D color diamonds often carry a higher premium due to their rarity and the fact they are nature's creation.
- Appreciation Potential: Historically, high-quality natural diamonds, especially those with D color grade, have shown a potential for value appreciation over time.
Authentication and Certification:
- Provenance: Authenticating a natural diamond involves tracing its origin, ensuring it's ethically sourced and conflict-free.
- Certificates: Reputable gemological labs provide certification for natural diamonds, indicating their authenticity, origin, and other essential attributes.
Lab-Grown D Color Diamonds
Creation Process:
- High-Tech Synthesis: Lab-grown diamonds are created in controlled laboratory environments using advanced technological processes like High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
- Time Frame: Unlike their natural counterparts, lab-grown diamonds can be produced in a few weeks to months.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations:
- Conflict-Free: Lab-grown diamonds are not mined, ensuring they don't contribute to potential conflict or exploitation.
- Eco-Friendly: Producing diamonds in a lab generally has a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional diamond mining.
Value Proposition:
- More Affordable: Lab-grown D color diamonds often cost less than their natural counterparts, making them more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
- Transparency: Modern consumers often appreciate the transparency and ethics associated with lab-grown diamonds.
Quality and Characteristics:
- Equivalent Beauty: A lab-grown D color diamond has the same physical, chemical, and optical properties as a natural D color diamond. To the naked eye, they are indistinguishable.
- Certification: Just like natural diamonds, lab-grown diamonds can also be certified by gemological labs, ensuring buyers are aware they are purchasing a lab-created stone.
In conclusion, both natural and lab-grown D color diamonds have their unique appeal and considerations. While natural diamonds carry the mystique of Earth's deep-seated history, lab-grown diamonds offer an ethically sound and often more affordable alternative. Regardless of the choice, understanding the distinction ensures informed purchasing decisions and an appreciation for the marvel that is the D color diamond.
Challenges and Considerations of D Color Diamonds
When delving into the world of D color diamonds, whether natural or lab-grown, there are challenges and considerations to bear in mind. Making an informed decision involves understanding these intricacies to navigate potential pitfalls and ensure the diamond's authenticity and value.
Here's a detailed exploration:
Price Premium:
- High Cost: D color diamonds command a significant premium given their rarity and perfection. This is especially true for natural D color diamonds.
- Value Proposition: Buyers should weigh the importance of owning the absolute highest color grade against potential savings with near-colorless diamonds that may appear very similar to the untrained eye.
Misrepresentation:
- Enhanced Diamonds: Some diamonds undergo treatments to improve their color grade. It's essential to ensure the diamond hasn't been artificially enhanced unless that's what you're seeking.
- Natural vs. Lab-Grown: With advancements in lab-grown diamond technology, distinguishing between them and natural diamonds can be challenging. Always seek certification to avoid potential misrepresentation.
Setting and Design:
- Color Enhancement: The setting can impact the perceived color of a diamond. For instance, a yellow gold setting might introduce color tints to a diamond, while platinum or white gold can enhance its colorless appearance.
- Size and Shape: Larger diamonds can make color variations more noticeable. Similarly, certain shapes might exhibit color differently.
Market and Resale Value:
- Natural Diamonds: Historically, high-quality natural diamonds have maintained or appreciated. However, the resale market can be complex, and immediate appreciation shouldn't be the primary reason for purchase.
- Lab-Grown Diamonds: The resale value and long-term market trajectory for lab-grown diamonds are still evolving. While they offer great initial value, their resale dynamics can differ from natural diamonds.
Ethical and Environmental Concerns:
- Mining Impact: Natural diamond mining can sometimes have significant environmental impacts and might be linked to conflict zones. Ethically sourced diamonds with certifications can alleviate some of these concerns.
- Sustainable Choice: Lab-grown diamonds offer a more eco-friendly and conflict-free alternative, aligning with the values of many modern consumers.
Certification and Authentication:
- Reputable Labs: Always ensure your diamond is certified by a recognized gemological laboratory (GIA, AGS, IGI for lab diamonds). This confirms its attributes and provides peace of mind.
- Grading Consistency: It's worth noting that grading can sometimes vary between labs. Always use the same lab for consistent grading if comparing multiple diamonds. As above I would only purchase diamonds with certificates from the GIA, AGS and IGI.
Embarking on the journey to acquire a D color diamond, one must approach with diligence, understanding the challenges and considerations involved. This ensures not just a wise investment but also a cherished possession that stands the test of time. Whether you're drawn to the allure of natural diamonds or the innovation of lab-grown ones, your purchase's true value lies in the joy and sentiment it brings.
Where to Buy D Color Diamonds
Navigating the world of diamond shopping can be overwhelming, given the plethora of options available. However, when it comes to D color diamonds, especially those of superior quality, certain retailers stand out from the crowd.
A CUT ABOVE® Collection Series:
- Premier Choice: When seeking the zenith of diamond quality, the A CUT ABOVE® Collection Series from Whiteflash is your best bet. These diamonds are the ultimate specimens, offering DEF IF-VVS super ideals, and they're unparalleled in their brilliance and craftsmanship.
- Comparison with Other Brands: While Blue Nile showcases its Astor Diamonds and James Allen offers the True Hearts brand, neither comes close to matching the impeccable standards set by the A CUT ABOVE® series.
Lab-Grown D Color Diamonds:
- Accessible Options: For those seeking affordability without compromising on the beauty of D color diamonds, lab-grown versions provide a viable alternative. Blue Nile and James Allen offer a commendable selection of these diamonds, although they tend to focus on the lower-priced, lower-quality spectrum.
- Premium Lab-Grown Selection: For connoisseurs who desire a lab-grown diamond that doesn't compromise on precision and beauty, Whiteflash's Precision Cut Lab-Grown Diamonds stand as a testament to craftsmanship and quality in the lab-grown category.
D color diamonds, with their pristine beauty and unmatched brilliance, represent the pinnacle of diamond quality. Whether you're seeking a natural diamond that's the product of billions of years of Earth's history or an ethically-produced lab-grown variant, it's imperative to choose a retailer that aligns with your values and expectations. The A CUT ABOVE® Collection Series remains unrivaled for those who accept nothing but the best, while Whiteflash's precision-cut lab-grown diamonds offer an eco-friendly alternative without compromising on excellence. Whichever path you choose, a D color diamond is more than a purchase; it's a lifelong treasure, an emblem of nature's beauty, and mankind's technological prowess.




